🟢 My Big Technology Framework - Part 2. The core engine and dealing with exponentials
For the next few weeks, I'm taking up the challenge of explaining all the mechanisms at play that lead a technological invention to become an innovation in the market. Which is probably more difficult than what physicists do when they try to explain the universe : )

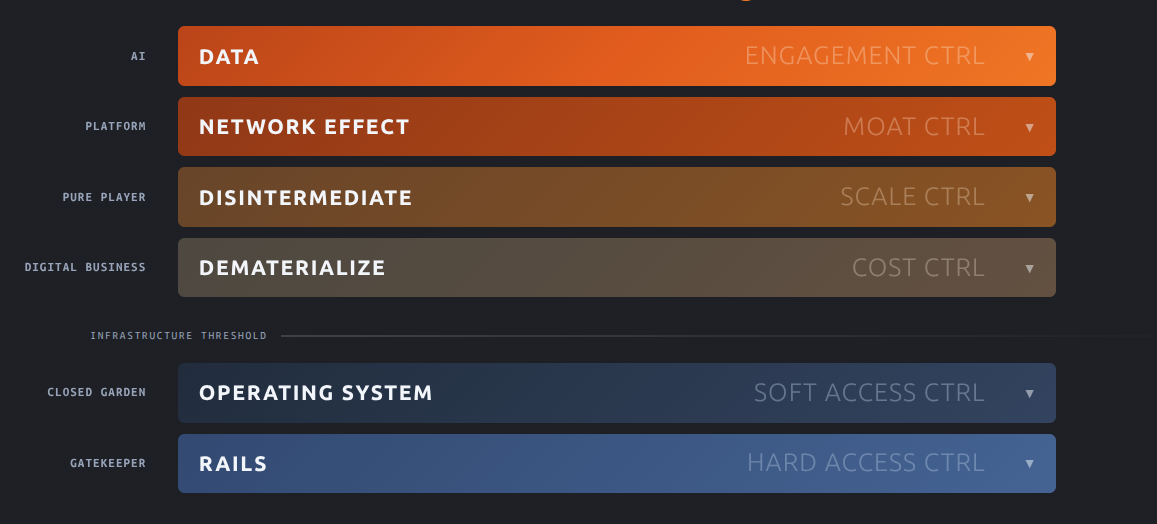
For this week, we'll zoom into the first step on the "core engine" about technology becomes innovation.

This core engine mostly is about three forces: the hype cycle, diffusion of innovation, and Moore's law. As in the past, I already addressed the first two forces, I thought it'd be better to focus more on Moore's law and, more broadly, what tech power laws mean...
- As a quick reminder, here's mostly what you need to know about using the Hype cycle framework:

- And how it's linked to the diffusion of innovation principle (here applied to an incubation program, but you'll get the general point):

Admittedly, these two first discussions are already quite a lot of things to digest, so let me try to get to the point with the extra layer of adding the influence of Moore's law all of the above...
What is Moore's law?
Initially, as you probably know, Moore's law states that the computing power of a microchip doubles approximately every two years, leading to exponential growth in computing power and efficiency. And although called a 'law,' this is anything but. It's rather a self-fulfilling prophecy invented by Intel in the 70s that somehow has still been followed up surprisingly well by chip manufacturers until now.